This article describes basic data with regard to the jack up rig elevation system, guides, pinion chord and leg fixation.
Jacking System
Firstly, let start with the jacking system , to lift and lower the hull, every Jack Up will have a special mechanism and the most basic of these is called ‘pin and hole’ (Figure 1); discrete leg positions will be used for the positioning of the hull. In the market today though, most Jack Ups will use a ‘rack and pinion’ (Figure 2) system to allow for continuous operation.

Figure 1 – Pin and Hole (Hercules offshore,2018)
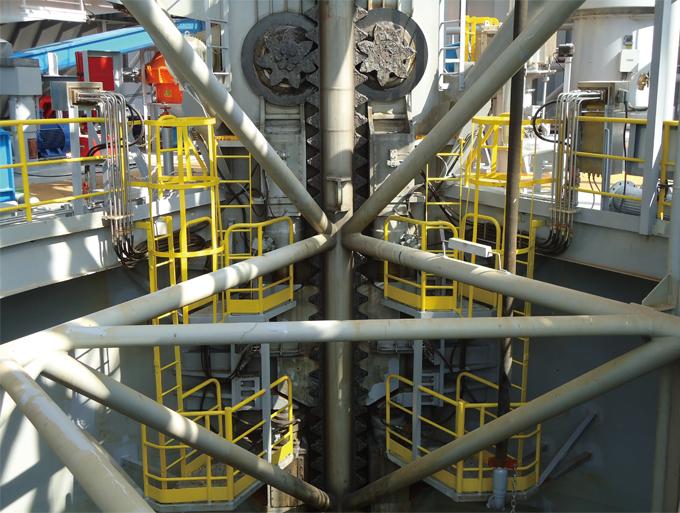

Figure 2 – Rack and Pinion (sagta.com,2018)
In terms of the jacking systems themselves, floating and fixed present the two main types. Whilst the fixed system goes for varied chord loading, floating attempts to equalize all chord loads using soft pads. In addition to this, you will also find hydraulic and electric power sources for the fixed type of system and both of these can equalize the chord loads for all legs despite achieving it in different ways.
Hydraulic – Essentially, this jacking system will look to keep the same pressure for all elevating units within a leg. At times, this can be a challenge because piping lengths, bends, and other issues can cause a loss.
Electric – Here, the motor speed will change as a result of the pinion loads and the speed-load characteristics. When jacking for significant periods of time, the equalizing occurs for all chords of each leg.
Upper and Lower Guides
In addition to lifting and dropping the hull, there is also a mechanism to ensure the legs go through the hull. For the pinion units, ‘bottoming out’ cannot occur on the rack teeth because the guides keep the pinions protected. With the upper and lower guides in place, even the deepest hulls or tall towers will be guided through safely. Ultimately, the only role of this mechanism is to ensure a steady length between the rack and the pinions; they are not involved in leg bending moment.
Just as we have seen throughout this guide, there are also different type of guides since some use the teeth to push against the tip whilst others focus on the chords. Known as ‘wear plates’, we should note that there are some guides that have been designed for replacement. Depending on the design, guides will also transfer leg bending moment as well as protecting the hull and pinions. Not all designs are equal; the extent to which moment is transferred is entirely dependant on the difference between the stiffness of the pinions and the guides.
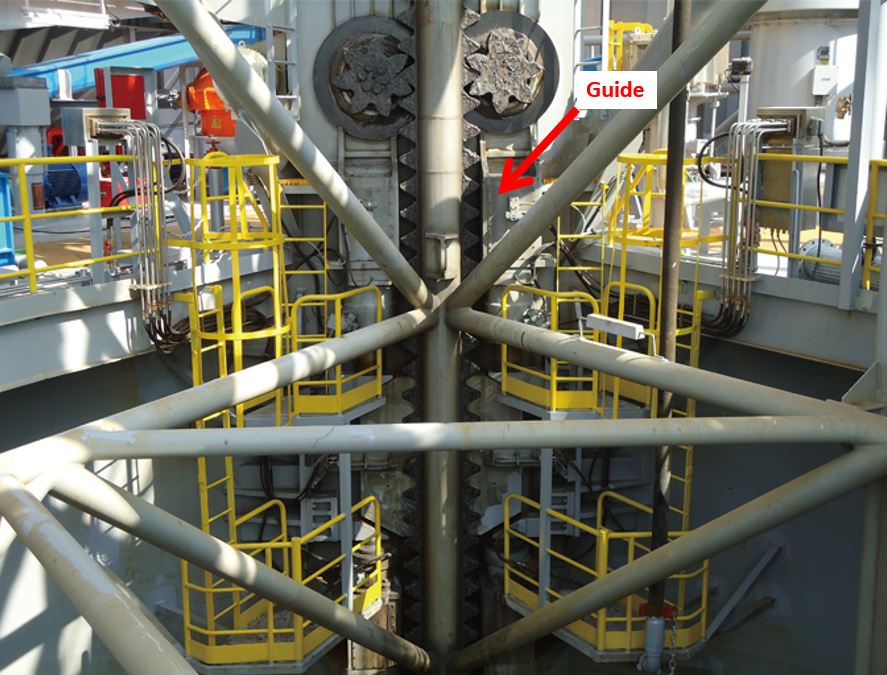

Figure 3 – Guide (sagta.com,2018)
Radial Pinion Chords v Opposed Pinion Chords
When a Jack Up has a rack and pinion elevating system, it will also boast an interface as either a single radial pinion or two different pinions at each chord. On the leg of the interface, both vertical and horizontal forces are exerted by jacking systems. Across the chord, the loads will be balanced by the opposed pinion systems which brings no additional horizontal load for the leg bracing. Thanks to the pinion arrangement and design, there will be a horizontal load on the leg bracing for radial pinions.
Opposed Pinions (3-Chorded Leg) – With opposed pinions, one chord will see rack and elevating systems on different sides which leads to double symmetry throughout. Essentially, the main advantage of having opposed pinion systems is that the pinions will share the load. Whenever the chord’s pinions are on the very same side, the jacking tower remains tall whilst the height reduces when the pinions are on two different sides.

Figure 4 – Opposed Pinions (3-Chorded Leg), (Kamel Elsayed – Slideshare, 2018)
To achieve a 50/50 share of the load in the pinions, they need to be arranged two high. To increase the distance between the smallest load and the largest, more pinions feature on the tower. Finally, we should also mention that the overall height reduction of the jacking tower with opposed pinions is an advantage because the wind load reduces as well as the weight. Figure 5 demonstrates the jack up rig with opposed pinions.

Figure 5 – A Jack Up with Three-Chorded Legs (eurasiadrilling.com, 2018)
Radial Pinions (4-Chorded Leg) – With this system, only one side will have rack and elevating pinions. As a result, only one plane of symmetry is seen in chords and the eccentricity causes bending from the net vertical pinion loads. If a Jack Up system has a radial pinion system in place, they will have two main advantages in comparison to the first example we saw. First and foremost, the upper guides are much further away from the lower guides because the height of the system is larger overall. Secondly, the leg chord generally experiences a lower drag coefficient because less hydrodynamic drag is created by one rack than two. Of course, designs vary greatly from one model to the next so the extent of this difference also changes. Figure 7 shows the jack up rig with radial pinions.
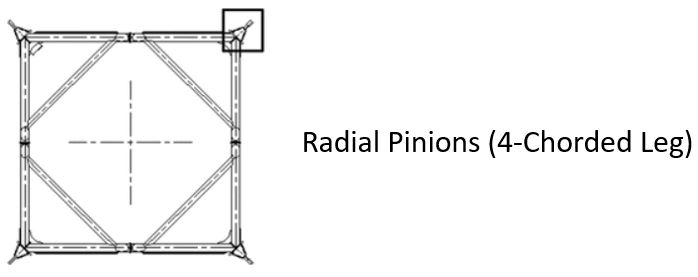
Figure 6 – Radial Pinions (4-Chorded Leg), (Kamel Elsayed – Slideshare, 2018)
Leg Fixation v No Leg Fixation
Finally, between the hull and the legs, the environmental, operational, and gravity loads need to be transferred by the Jack Up units. With some options, they will use pinions and a fixation system before then transferring this rather than using elevating pinions which is something that other units will use.
With leg bending moment, there are also two types that can occur; horizontal couple or vertical couple. As the names suggest, the first uses the lower and upper guides while the second relies upon varying chord loading. Depending on the stiffness values, there will be a different moment proportion transferred. With a leg fixation in place, the proportion of the moment transferred will be higher and it transfers as a vertical couple.
As mentioned in the title of this section, there are also units with no leg fixation and these need heavier bracings in order to react to the loads of operating, survival, and tow leg-to-hull. During this process, extreme caution must be taken since the only holding or locking mechanism comes from the jacking unit. Whenever there is a drop in holding or jacking capacity, this is likely to impact other units and will increase the load on the leg structure. In the past, we have seen the ability to handle higher loads with higher braces but there is still a knock-on effect and this time it comes with the increased wave, wind, and current loads. When this happens, the environmental ratings are much lower than seen in units with a fixation system. In these rigs, therefore, there is an importance upon the balance between the strength of the brace and the chord.
In terms of pinions, these are reduced with a leg fixation system. Considering the increased stiffness when compared to guides, a vertical couple is seen with leg/hull moment transfer too which negates the need for so many brace scantlings. In turn, the leg will weigh significantly less and less drag is produced thus improving the environmental capabilities of the unit in question. All things considered, this leads to a boost in the unit’s ability to tow with fully-retracted large leg lengths. If service is ever required, support can be given to the rig by the fixation system but, when an accident occurs, the leg bracing is often considered the most prone feature to damage!
References
Sagta.com (2018). Jack up system – Products – sagta. [online] Available at: http://www.sagta.com/index.php/Eng/article/listPage/parentID/2/cat_id/39 [Accessed 24 Aug. 2018].
Hercules 208 General Information (2014). 1st ed. [ebook] Houston: Hercules Offshore, p.1. Available at: http://www.herculesoffshore.com/pdfs/rigs/H208%20Spec%20Sheet%20rev.03%20August%2022%202014.pdf [Accessed 24 Aug. 2018].
Slideshare.net (2018). The Road to Saqqara ( Jack-up units and Move ). [online] Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/kemo44/the-road-to-saqqara-jackup-units-and-move [Accessed 25 Aug. 2018].
Eurasiadrilling.com (2018). Jack-up rigs. [online] Available at: http://www.eurasiadrilling.com/operations/offshore/jack-up-rigs/ [Accessed 18 Aug. 2018].
Enscoplc.com (2018). Ensco plc – Global Operations – Rig Fleet. [online] Available at: https://www.enscoplc.com/global-operations/rig-fleet/default.aspx [Accessed 18 Aug. 2018].
Source: Dilling Formulas and Drilling Calculations



Would you please let me know what is the main purpose for fixation system